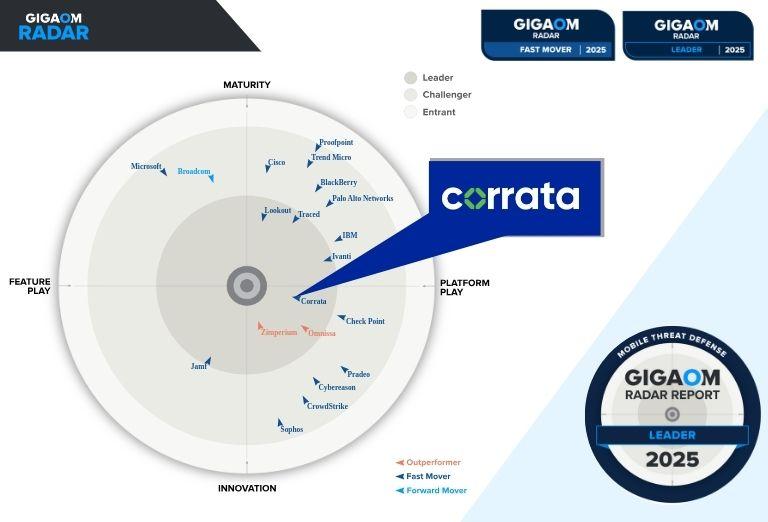
Corrata’s Top 5 Cyber Security Predictions for 2019

Following an eventful year in the world of cyber security, what can we expect in 2019?
2018 was a eventful year for technology and the world of cyber security. Privacy and the security of personal data was the main topic of discussion. This is following major changes in legislation and multiple high-profile data breaches around the world. Phishing attacks grew more sophisticated. The spread of malware via mobile apps exploded. Machine learning emerged as a potential security tool. All of these trends further reinforce that protection for enterprise mobile devices is more important than ever. For our full Year in Review of 2018, check out our most recent blogpost. However, now it is time to turn our attention towards the year ahead and what to expect for 2019. Following the events and developments of 2018, we anticipate 2019 to be another eventful year for mobility and cyber security. Read on to find out our top 5 cyber security predictions for 2019!
1. Mobile will continue to reign
In 2018 we reported that mobile device usage was at an all-time high as a result of expanding networks, reduced costs, and greater accessibility on a global scale. And as more and more businesses recognize the value of mobility and employees increasingly use mobile devices for work, this number will continue to grow. Cisco recently estimated that global circulation of mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets would reach 6.2 billion devices by 2021 and we predict that 2019 will have a large part to play in reaching this number. However, this influx of devices and the increased reliance on mobile will lead to greater risks for enterprises in 2019. The lines between work and personal continue to blur. We are fast approaching a position where mobile security must become a crucial element of organizational strategy.
2. Privacy will remain a major issue
2018 saw a huge emphasis on the security and privacy of personal data collected by organizations. Following the introduction of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe in mid-2018, organizations all over the world have been forced to examine their data collection and processing practices in order to ensure compliance with the new rules and avoid prosecution. Because of this new legislation and after the emergence of several high-profile data leak scandals, internet users, employees, and consumers have all now become hyper-aware of the security of their personal data and are holding organizations accountable for their mistakes.
As the GDPR grace period draws to a close, multiple commentators are predicting that 2019 will see the first high-profile crack down on a breach of the new regulations. This is likely to have major ramifications for the rest of the world as the outcome of this case will set the precedent by which all future breaches will be judged and will give companies an idea of just how strictly these new rules will be enforced, as well as how harsh the fines will be.
3. Increased targeted spear-phishing
Phishing attacks have existed for many years in many different forms. Recently however, attacks have moved away from generic emails towards more personalized campaigns. This is a trend we predict to increase rapidly in 2019. Phishing attacks in the past generally consisted of hackers sending batches of emails with generic links to multiples users. Phishing attempts now tend to be much more targeted and personalized. ‘Spear-phishing’ campaigns have become extremely sophisticated today thanks to the plethora of personal and identifying information readily available online. Platforms like social media and messaging services (WhatsApp, Facebook) have made it much easier for malicious actors to pose as legitimate bodies, luring users into a false sense of security to fall for phishing attacks. Spear phishing is likely to rise to an all-time high in 2019 as it becomes easier to obtain information from users online and therefore easier to build a convincing attack.
4. Machine learning will become key
2018 was a significant year in the development of artificial intelligence. In particular, we saw the use of machine learning technology by both cyber attackers and defenders. We predict that this trend will intensify in 2019. The use of ‘zero-day’ phishing attacks – campaigns created, deployed, engaged, and dissolved all in a time-frame as short as a single day – is continuously increasing making it harder for traditional anti-virus solutions to keep up. However, there is some good news. We believe that machine learning will also become a key element in the fight against cyber-crime in 2019 by using a process of continuous learning and improvement in order to preemptively anticipate, detect, and eliminate these threats as they are created.
5. Cyber education will be critical
The cybersecurity skills gap of individual employees will become a critical aspect of 2019. In 2018 it was reported that 63% of businesses lacked the skills required to avoid the threat of cyber-attacks and that poor knowledge of organizational security could have serious financial repercussions on a business. Training employees to recognise the indicators of malicious or legitimate sites and messages is half the battle in preventing attacks however as campaigns become more sophisticated, the issue is only set to worsen if proper training and education is not provided.
Guaranteed to have its ups and downs, we believe 2019 will be an extremely busy year for cyber security. From privacy to phishing, this coming year will likely have a significant, long-lasting impact on the industry as a whole. We here at Corrata can’t wait to be a part of it!
To find out more about Corrata’s solution, visit www.corrata.com or email us at info@corrata.com.
And for more industry news, insights and analysis – follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn!