User Credentials – Protecting the Keys to the Castle

Protecting user credentials on smartphones and tablets is now crucial for SMBs as remote working becomes the ‘new normal’
In today’s world, we’re constantly bombarded with security warnings about the dangers of cyber threats and data breaches around leaked user credentials. Thankfully, when using our traditional IT systems, we’re protected from phishing attacks with the help of cybersecurity systems like email gateways, firewalls and web filters.
But, the pandemic has forced businesses, both large and small, to migrate to remote work. What protection do we have on our company mobile devices and tablets? Do we even need security on our remote devices? The short answer is absolutely.
Company size doesn’t matter to hackers
Maybe you’re thinking, “so what if someone knows my password to X? There’s nothing sensitive in there that they could harvest”. Or, “my company is small…a cyber criminal wouldn’t bother coming after us.”

The truth is, credential theft is just as serious for small businesses as it is for larger organizations. Cyber criminals do not discriminate when it comes to their next opportunity. In fact, according to Hiscox, 43% of attacks are aimed at small businesses.
Targeting remote workers
VMWare reports that 91% of businesses have seen an increase in cyber attacks as a result of employees working from home. Without security protection on smartphones and tablets, businesses are exposed to credential theft and data breaches.
Further studies reveal there has been a 50% increase in mobile vulnerabilities since COVID-19, highlighting the dangers of blurring lines between corporate and personal networks. In fact, according to Corrata’s research team, 11 mobile threats are encountered per device per month on average.
Consequences
Think of all the software systems that require access via username and password. Even if employees don’t use all of these applications on their smartphone, a password leak is all that is required to infiltrate company software.
For example, imagine a hacker penetrates the company CRM and steals all of their customer data. What if the hacker goes a step further and wipes the database completely? Without a backup system in place, companies have no way of recovering this data.

Or, consider a situation where WordPress credentials are leaked causing an entire E-commerce website to go down. Disappearing from search engines for even a few hours can have detrimental consequences for businesses.
User credentials are the keys to the kingdom and protecting usernames and passwords should be a number one priority for every business regardless of the device employees are using.

What tactics are hackers using?
Phishing
One of the most dangerous and effective methods for stealing passwords is phishing and its variants (smishing, vishing). In fact, phishing is now responsible for almost one quarter (22%) of data breaches. Hackers are cunning and take advantage of global trends. For example, COVID related phishing attacks rose by 667% as criminals preyed on universal fear and the quest for information.
Smishing
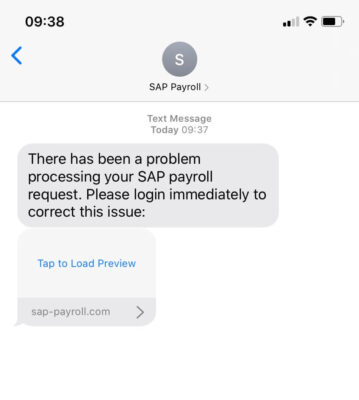
Smishing (SMS phishing) attacks are becoming increasingly more frequent. The open rate of a phishing link over SMS is 98% compared to 20% over email. Imagine that the finance director of a small accounting firm receives a text alerting him to a problem with payroll approval. Caught off guard, he clicks on the link and enters his log in details to investigate. Unknowingly, he has just handed over complete system access to a hacker.
Phishing via social media
Social media is becoming a popular tool for companies to interact and engage with clients and partners. Imagine how easy it would be for a hacker to create a fake LinkedIn account, send an InMail to their victim and harvest their credentials through a phishing link. Companies without a proper mobile security solution in place are vulnerable to attack.
Mobile malware
Another tactic is to use mobile malware to extract credentials from a users phone. It’s easy to imagine how an unsuspecting employee could be tricked into downloading a malicious app masquerading as a game or an entertainment service. Once on the phone, the malware has multiple ways of extracting credentials: reading messages, inserting a fake login page or requesting a passcode.
Protecting user credentials
As a basic first step, follow good password hygiene and implement regular security training for all staff. However, as we all know, cyber criminals will use any gap in a company’s defenses to harvest credentials. That’s why it’s critical for businesses to have a mobile security solution in place like Corrata.
Corrata’s mobile security solution prevents phishing, malware and WiFi attacks on company smartphones and tablets, spots misconfigured devices and allows businesses to filter inappropriate apps and content. So, with your employees working remotely, you can be confident with Corrata installed that all company mobile devices are safe from attack.