Pegasus, Graphite, Predator, Hermit Spyware – NSO and its clones

Commercial spyware: it hasn’t gone away
For a brief moment, it looked as if the commercial spyware industry was on the back foot. Successful legal suits by Meta and others appeared to have fatally undermined the business models of vendors such as Intellexa and the better-known NSO Group. However, evidence is mounting that the industry may be getting a second wind. In recent months, both Apple and Google have issued multiple releases specifically tagged as addressing “known exploited vulnerabilities”.
Further evidence of the industry’s resurgence comes from recent procurement filings showing that U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) will soon gain access to technology developed by spyware vendor Paragon. This follows the Trump administration’s decision to lift a pause on a $2 million contract. The deal, first signed in late 2024 under the Biden administration, had been suspended pending a compliance review to ensure it complied with an executive order limiting U.S. government use of commercial spyware.
Paragon is best known for its Graphite spyware, which has been documented in multiple campaigns targeting civil society actors. According to public procurement records, ICE will be the contracting agency. The significance of this move cannot be overstated: for the first time, a U.S. law enforcement body will officially procure technology and services from one of the world’s most advanced spyware platforms. This marks a major shift in U.S. policy, underscoring both the demand for these tools and the difficulties governments face in restricting their use even after pledging reforms.
How ICE will use Paragon’s capabilities remains unclear, but an educated guess is that it will be deployed to track and apprehend undocumented migrants. Historically, spyware exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities has been reserved for highly targeted attacks due to the rarity and value of such exploits. Broader community-level campaigns, such as China’s surveillance of Uyghurs, have typically relied on less sophisticated methods.
The days when NSO Group’s notorious Pegasus software was the only game in town are long gone. Google’s February 2024 report, *Buying Spying – Insights into Commercial Surveillance Vendors*, underscored the scale of the spyware industry. The report noted that the emergence of these vendors has created “a lucrative industry used to sell governments and nefarious actors the ability to exploit vulnerabilities in consumer devices… enabling the proliferation of dangerous hacking tools.”
In January 2025, Michael Casey, then head of the U.S. government’s counterintelligence agency, stated that “nearly 100 nations” have purchased advanced spyware capable of infiltrating mobile phones. He added: “Everyone knows about the NSO Group, but there are dozens of these companies.” Google now tracks around 40 commercial spyware vendors of varying sophistication and visibility. A spyware incident database cataloged 19 disclosed cases in 2022 alone, involving not just NSO but also Cytrox, Quadream, an…
Despite significant U.S. government actions – including the blacklisting of NSO in November 2021, export restrictions on Cytrox and Intellexa, and visa bans on spyware abusers—the spread of these tools continues.
A spate of spyware incidents
Since late 2021, multiple stories have highlighted the activities of the surveillance-for-hire industry. The flurry of news began when researchers at the University of Toronto’s Citizen Lab released findings from its investigation into Predator spyware, produced by North Macedonia-based Cytrox. Citizen Lab identified likely Predator customers in Armenia, Egypt, Greece, Indonesia, Madagascar, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and Serbia. This announcement coincided with Meta’s disclosure that it had banned seven surveil…
In June 2022, Hermit spyware—developed by Italian firm RCS Labs—came to light. Predator has also been implicated in an ongoing and politically explosive hacking controversy in Greece, described by Politico as “a scandal that has spiraled into Greece’s own version of the U.S.’s 1972 Watergate intrigue.” As more scrutiny has been applied to this murky industry, it has become clear that NSO’s Pegasus is just one element in a much broader global cyber-mercenary market.
2022 also marked the first reports of Paragon’s Graphite spyware, with the New York Times noting its use by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration. In June 2025, Citizen Lab published the first forensic confirmation of Graphite following an investigation into an incident involving European journalists.
Surveillance technology has a long history. Elizabethan England’s security services were adept at opening sealed correspondence undetected. More recently, Edward Snowden revealed the NSA’s mass surveillance of global communications networks. The rise of end-to-end encrypted messaging apps such as WhatsApp, Signal, and Telegram rendered traditional network surveillance less effective. To fill the gap, vendors such as NSO developed spyware to provide direct access to the unencrypted content on mobile devices…
Vulnerabilities and Exploits
For those of us working in mobile endpoint security, the most interesting element of these reports is the hard evidence they provide of successful exploits against mobile software. Unlike off-the-shelf malware, which relies on tricking users into granting dangerous permissions (for example, screen overlays or message interception), advanced spyware is invisible to the end-user and easily evades antivirus software. This is exactly the type of threat mobile endpoint security solutions are designed to mitiga…
Broadly speaking, software vulnerabilities fall into two categories: zero-day and n-day. Zero-day vulnerabilities are unknown to the software vendor and are the most dangerous, as even fully patched devices remain exposed. N-day vulnerabilities, by contrast, are known to vendors and generally fixed in the latest software updates. However, sometimes their severity is overlooked, delaying patches. N-day vulnerabilities remain significant because only a minority of devices are ever fully up to date. Cytrox, t…
In June 2022, Google confirmed the discovery of Hermit spyware for both Android and iOS, developed by RCS Labs. Victims were identified in Italy and Kazakhstan, with researchers suggesting the spyware targeted anti-government protesters in Kazakhstan. The iOS version exploited four n-day and two zero-day vulnerabilities—all since patched by Apple. Google could not provide a full analysis of the Android variant, which masqueraded as a Samsung app. The initial download did not contain exploits but tricked us…
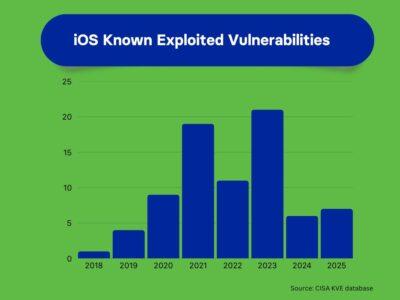
Trend in Known Exploited Vulnerabilities for iOS
So far this year, Apple has disclosed seven known exploited vulnerabilities (KEVs) for iOS—a figure already higher than the total for 2024. CISA maintains a database of KEVs, defined as vulnerabilities with credible evidence of in-the-wild exploitation. KEVs are identified in several ways: researchers may flag them, Apple’s telemetry may reveal evidence of exploitation, or forensic analysis of a compromised device may confirm their use.
Of the 13 KEVs patched by Apple since 2024, many were identified by Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) and Citizen Lab, both of which have strong reputations for spyware investigation. Google’s *Buying Spyware* report noted that half of the zero-day exploits used against its products were attributable to commercial spyware vendors. It also linked nine iOS KEVs to vendors including NSO Group, PARS Defense, Intellexa, and Variston. The steady stream of exploits is almost certainly a byproduct of the spyware…
What’s lurking in the shadows?
The work of digital privacy organizations, NGOs, security researchers, and oversight bodies has given us valuable insights into spyware capabilities—but much remains hidden. Most public reporting focuses on government use against political opponents. Far less is known about in-house spyware built by state agencies, and almost nothing about use by cybercriminals or hostile nation-states.
What we do know is troubling. Multiple commercial vendors now offer Pegasus-like tools. Google’s TAG is tracking more than 40 surveillance vendors, and it is naïve to assume nation-states and cybercriminals do not also have access. Moreover, recent disclosures show spyware is no longer limited to political surveillance but is now a tool for industrial espionage. Black Cube, one of the entities banned by Meta, counts customers in medical, mining, energy, telecom, high-tech, legal, financial, and real estate…
These revelations confirm that spyware can exploit iOS and Android vulnerabilities to gain remote access to phones’ full capabilities—including audio, messaging, and cameras. In an era of renewed geopolitical tension—Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, conflicts across the Middle East, and shifting alliances during Trump’s second presidency—the risks are growing. Cyberweapons are being used against civilian infrastructure as well as for financial gain.
The conclusion is clear: attackers have both the motivation and the capability to target your employees’ mobile devices. The threat posed by sophisticated spyware has never been more acute. Vigilance must be your watchword.




